Abstract
Background
Atypical HUS (aHUS) is a rare thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) caused by complement dysregulation. Eculizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting against complement factor C5. Ravulizumab, a longer acting C5 inhibitor developed through minimal, targeted modifications to eculizumab was recently approved for treatment of aHUS in 2019. Here we describe the clinical presentation, laboratory, genetic profile, treatment along with long-term sequelae of patients diagnosed with aHUS. The outcomes of restrictive use of eculizumab and the use of ravulizumab were also studied.
Materials and Methods
We conducted a single center retrospective cohort study, searching electronic medical records of patients diagnosed and treated for aHUS at University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, from January 1, 2013 to January 31, 2021, after IRB approval. Inclusion criteria :1) Presence of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA) with thrombocytopenia 2) ADAMTS13 activity > 10 % 3) Age > 18. Exclusion criteria: 1) Age < 18 years 2) TMA associated with hemolytic uremic syndrome, scleroderma renal crises, anti-phospholipid syndrome.
Results
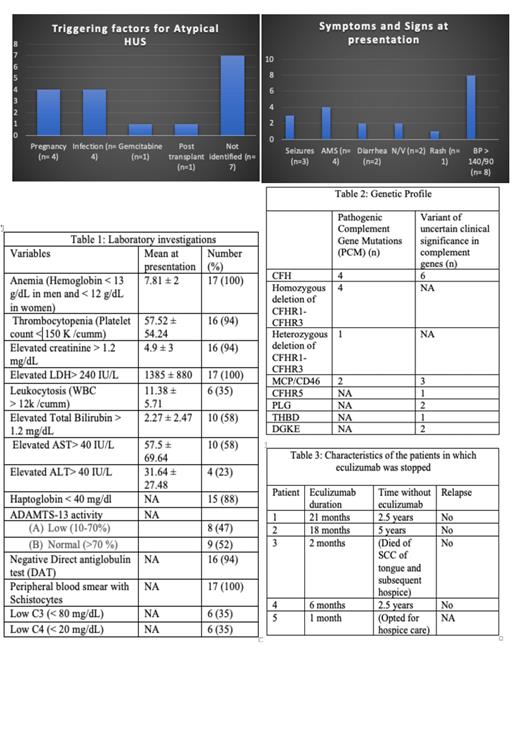
Seventeen patients meeting the inclusion criteria were enrolled in the study. The mean age at diagnosis was 47.4 ± 17.9 years. Most of the patients were Caucasians (n=10, 58%) and females (n= 14, 82%). All the patients except one had acute kidney injury (AKI) at presentation (n=16, 94.1%), the most frequent extra-renal presentation was CNS involvement -seizures, confusion and altered mental status (n= 7, 41.2 %) followed by Gastrointestinal- non-bloody diarrhea, nausea and vomiting (n=5, 29.4 %) [Figure 1]. Lab investigations are described in [Table 1]. Complement genetic testing was done in 100% of study population. Factor H related genes 1/3 (CFHR1/3) and complement factor H (CFH) were the most commonly found pathogenic mutations [Table 2]. In this study, pregnancy and infection (n= 4, 23.5% each) were identified as the most common triggers [Figure 2]. For two of the patients, it was the first pregnancy and for the other two, it was their second and third pregnancies. They presented at the second, sixth, and sixteenth week postpartum respectively.
Eleven (64.70%) patients developed chronic kidney disease (CKD) with six (35.29%) patients progressing to end stage renal disease (ESRD). Two (11.76 %) pregnant patients developed cardiomyopathy, two (11.76%) patients developed pulmonary complications (pneumonia and pulmonary hypertension) and three (17.64%) patients developed epilepsy. All the postpartum females in our study were able to breastfeed while on eculizumab with no long-term complications in the neonates. One patient had two subsequent deliveries with no ante, intra, or post-partum consequences or repeated triggers of aHUS.
Fourteen patients (82.3%) received therapeutic plasma exchange, four (23.5%) patients received iv methyl prednisone (1mg/kg) and two (11.7%) patients received IVIg prior to initiating eculizumab. Over time, five (29.41%) patients opted to completely stop drug therapy and four patients (23.52%) chose to shift to ravulizumab because of the ease of treatment duration (every 8 weeks rather than every 2 weeks for eculizumab). All these nine patients remained in remission with stable hematologic and renal parameters on subsequent follow-ups [Table 3]. Three patients (17.6 % mortality) died in our study due to causes unrelated to aHUS.
Conclusions:
The clinical diagnosis of atypical HUS can be challenging especially with extra-renal manifestations. Females were four times more affected than males. PCMs were present in 11 patients. Early diagnosis and treatment with C5 inhibitors improves morbidity and mortality. The decision to discontinue or switch eculizumab to ravulizumab will likely decrease healthcare costs and improve patient compliance but should be based on disease severity.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal